Learn how to fix the "DNS Server Not Responding" error with 10 troubleshooting methods or use a VPN for quick access. Fix it quickly and access websites again.
In daily use of the Internet, users often encounter various connection problems, among which DNS server not responding is a common fault. Even in the latest Windows 11 system, you may encounter the problem of Windows 11 DNS server not responding.
So, what causes the problem of "DNS server does not respond"? How to fix DNS server not responding? Next, this article will explore the possible causes and solutions together.

When you try to access a website, if you see an error message like "DNS server not responding", it means that your computer cannot find the IP address of the target website through domain name resolution. This will prevent you from accessing the website, opening web pages, sending emails, or using certain online services. In serious cases, it may even affect the normal use of the entire network, affecting work and entertainment experience.
The problem of "DNS server not responding" is usually caused by the DNS server's inability to resolve the domain name normally or the connection is interrupted. Possible reasons include network configuration errors, DNS server failures, router problems, or ISP service failures, etc. Then, the DNS server not responding how to fix? Keep reading.

Fortunately, in most cases you can solve this problem or even DNS server not responding WiFi issues with some simple operations. Whether it is to modify the DNS server address or check the local network settings, the method to fix the "DNS server not responding" problem is actually not complicated. Next, this section will provide you with a series of effective solutions to help you restore normal network connection and allow you to surf the Internet smoothly.
1. Switch browsers
Try to access the website through a different browser, such as switching from Safari or Google Chrome to Mozilla Firefox or Microsoft Edge. If the problem is solved after switching, you may need to update or reinstall the browser. If the problem persists, the browser is not the cause.
2. Use other devices
Use another device (such as a mobile phone) to access the same website to see if it can be opened normally. If using a mobile phone works, it may be a problem with the current device.
3. Start the computer in safe mode
By starting a Windows or macOS device in safe mode, limit the programs and services running, and help rule out whether the connection problem is caused by the operating system or third-party software. If you can access the website normally in safe mode, it may be that a program is interfering with the network connection.
4. Temporarily disable antivirus software and firewalls
Antivirus software and firewalls may hinder network connectivity. Try disabling them and accessing the website again. If the problem is solved, you can try changing the antivirus software or adjusting the firewall settings. Remember to re-enable the security software after completion.
5. Disable secondary connections
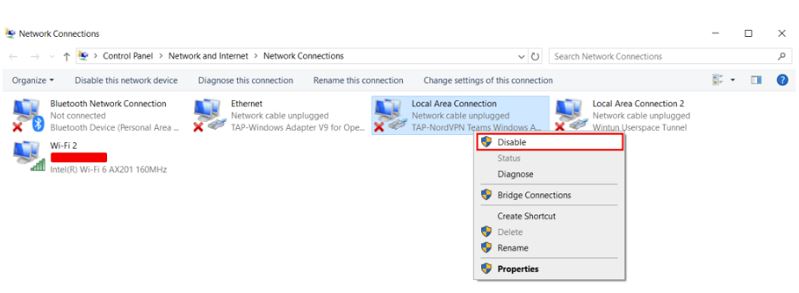
Disable unused network connections on your device to ensure that only the current connection is active. Disable other connections in Windows through the Network Connections settings and in macOS through the Network settings. After disabling unused connections, restart the browser and try accessing the website again.
You May Like: How to Run DNS Leak Test On PC >>
6. Disable the Windows peer-to-peer feature
In Windows 10, the peer-to-peer feature may interfere with DNS connections. It allows devices to share Windows updates over a local area network, which may affect the DNS process. Disabling this feature may help resolve the "DNS server not responding" issue.
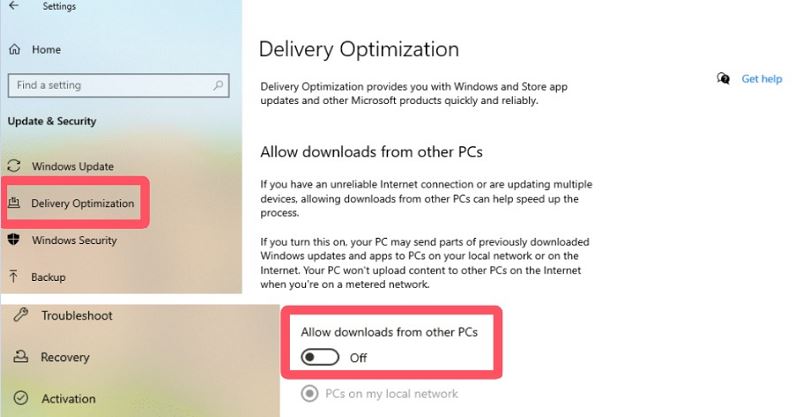
Go to Settings > Update & Security > Delivery Optimization, turn off the "Allow downloads from other PCs" option, restart your computer, and check if the problem is resolved.
 7. Restart your router
7. Restart your router
Restarting your router can flush its cache and possibly resolve DNS issues. Most routers have a power button that you can press and wait a minute before restarting. If the problem persists, try restarting the router completely by unplugging the power cord completely, waiting 30 seconds, and then plugging it back in.
8. Update your network adapter drivers
Outdated network adapter drivers can cause DNS connectivity issues. Update your drivers manually or using an automated tool like Driver Easy or Snappy Driver Installer. After the update, restart your computer and check if your network connection is back to normal.
9. Flush your DNS cache and reset your IP
Clearing your DNS cache and resetting your IP settings can sometimes resolve connectivity issues. In Windows, open a command prompt and type "ipconfig /flushdns" and press Enter.
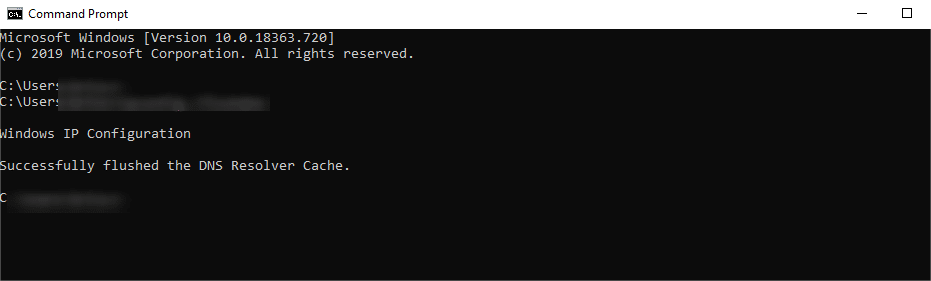
Mac users can refresh DNS by entering the corresponding command in the terminal. Once completed, try to reconnect to the Internet.
Also Read: How to Solve “This Network is Blocking Encrypted DNS Traffic” Error >>
10. Disable IPv6
The IPv6 protocol sometimes causes the "DNS server not responding" error. You can try to disable it to solve the problem.
In Windows, right-click the current network connection, select "Properties", and uncheck the "Internet Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IPv6)" option. In macOS, you can disable IPv6 for wireless or Ethernet connections through the terminal command, refresh the browser, and check if the problem is solved.
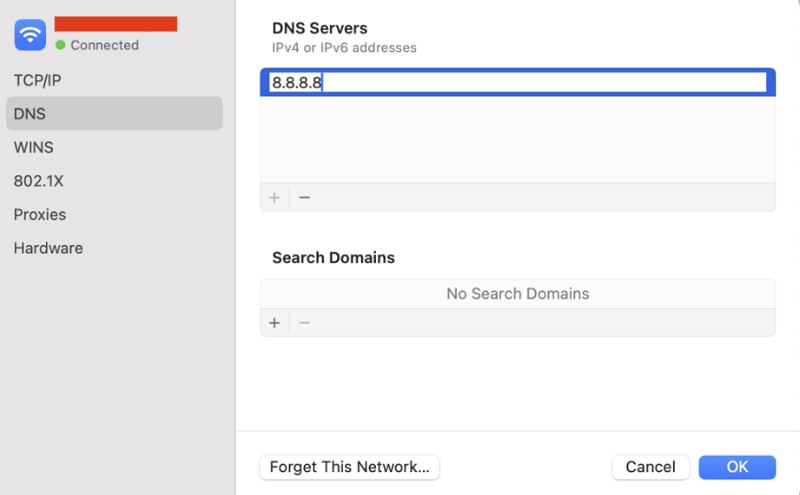
11. Change the default DNS server
If there is a problem with the DNS server, you can try to change the default DNS server in Windows.
Go to the network connection properties, select the adapter you are using, click "Properties" and select "Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)". Then, manually enter the DNS address, such as Google's DNS address (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4). In macOS, modify the DNS settings through "System Preferences" > "Network" > "Advanced". After modifying, restart the browser and try to access the website.
You might not expect that using a VPN is also an effective troubleshooting method for the "DNS server not responding" problem.
A VPN bypasses the local DNS resolution process by encrypting your network traffic and directing it to a remote server. When a local DNS server fails or does not respond properly, a VPN can resolve domain names through its own DNS service, thereby avoiding reliance on the local network's DNS server. This means that even if your local DNS server is not working properly, you will most likely be able to access the Internet normally after using a VPN.
The principle of a VPN is based on its mechanism of redirecting network traffic to an external server, mainly to solve the situations where you cannot access a website due to DNS configuration problems. By connecting to a speed VPN server in a different region, you can also switch to a more stable or faster responding DNS server. However, if the DNS server is not responding for other reasons, then the VPN will be powerless.
Since a VPN can indeed help solve the DNS server not responding problem caused by DNS configuration alone, and can also provide you with additional network security and anonymity, how to choose to use a VPN for specific operations?
If you just want to use a VPN to try to solve this problem, and the daily use of a VPN is not so much, it is recommended that you choose a trustworthy free VPN for quick verification. The free version of iTop VPN is a good choice. If you have more use needs for a VPN in the future, you can consider choosing the one that suits you best from the best VPN for Windows to try.
To quickly verify the effectiveness of this VPN method, you can use a trustworthy and secure free VPN tool, such as iTop VPN. iTop VPN offers a free version that allows you to connect to dozens of free VPN servers, switch DNS settings, and help troubleshoot network problems caused by local DNS problems.
iTop VPN's free features and DNS-related information:
Free connection: iTop VPN offers dozens of free server options, allowing you to freely switch network locations and help solve DNS problems.
DNS protection: iTop VPN has built-in DNS configuration functions, so you can avoid local DNS configuration errors and connect directly to stable remote DNS servers.
Privacy and DNS leak protection: iTop VPN provides encrypted network traffic and DNS leak protection to ensure your data security and avoid DNS leaks.
Avoid ISP DNS restrictions: Sometimes, the DNS servers of Internet Service Providers (ISPs) have problems, and using a VPN can avoid this.
No ad interference: The free version of iTop VPN does not contain intrusive ads, providing a smooth user experience.
Step 1. Download and install the iTop VPN version for Windows or macOS.
Step 2. Once installed, open iTop VPN and select a free server to connect to.
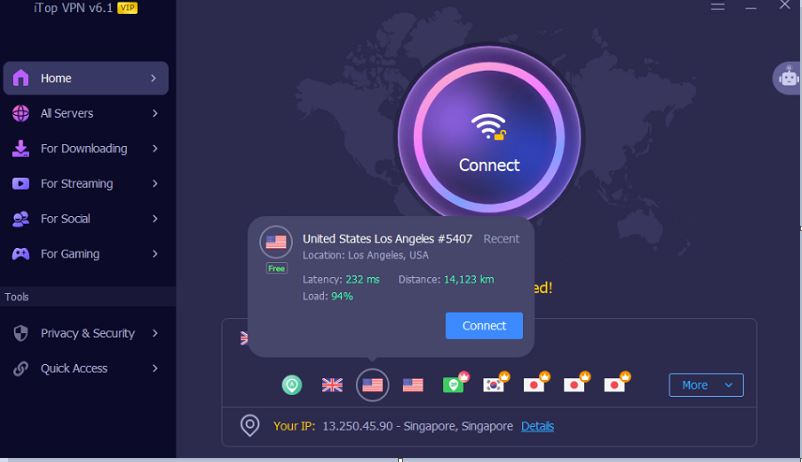
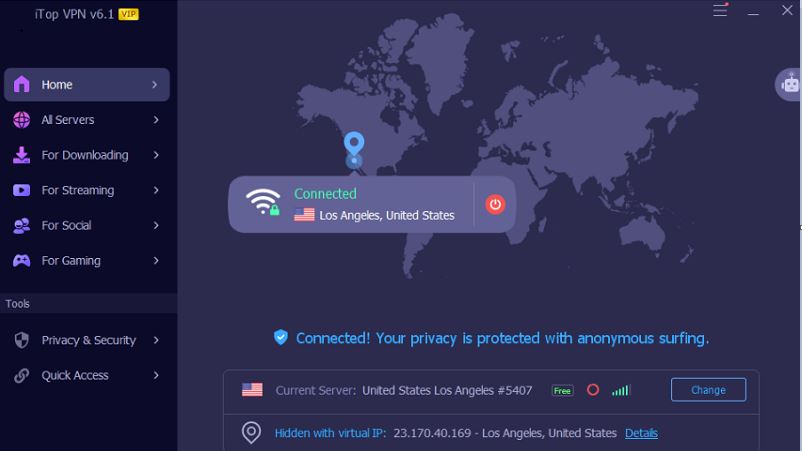
Step 3. After connecting, try to access the website you were unable to access before. If the problem is resolved, it means that the DNS configuration is indeed the root cause.
The Bottom Line
In summary, the "DNS server not responding" error may be caused by a variety of reasons. Through a series of troubleshooting steps, such as switching browsers, clearing DNS cache, modifying DNS settings, etc., you can solve this problem more effectively. In addition, using VPN as an alternative is an effective means worth trying. VPN can bypass the local DNS server and use a stable remote DNS service to restore network connection. If the problem persists, it is recommended to contact the network service provider for further diagnosis and support.
10+ free servers in US, UK...
3200+ extensive servers
Dedicated IP addresses
Ad blocker and Proxy service
For Windows 11/10/8/7